Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context, and Africa has a large quantity of natural resources.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa is also heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them "oral civilisations", contrasted with "literate civilisations" which pride the written word. African culture is rich and diverse both within and between the continent's regions, encompassing art, cuisine, music and dance, religion, and dress.
Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted to be the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade, also known as the great apes. The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, and Homo sapiens (modern human) are believed to have originated in Africa 350,000 to 260,000 years ago. In the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE Ancient Egypt, Kerma, Punt, and the Tichitt Tradition emerged in North, East and West Africa, while from 3000 BCE to 500 CE the Bantu expansion swept from modern-day Cameroon through Central, East, and Southern Africa, displacing or absorbing groups such as the Khoisan and Pygmies. Some African empires include Wagadu, Mali, Songhai, Sokoto, Ife, Benin, Asante, the Fatimids, Almoravids, Almohads, Ayyubids, Mamluks, Kongo, Mwene Muji, Luba, Lunda, Kitara, Aksum, Ethiopia, Adal, Ajuran, Kilwa, Sakalava, Imerina, Maravi, Mutapa, Rozvi, Mthwakazi, and Zulu. Despite the predominance of states, many societies were heterarchical and stateless. Slave trades created various diasporas, especially in the Americas. From the late 19th century to early 20th century, driven by the Second Industrial Revolution, most of Africa was rapidly conquered and colonised by European nations, save for Ethiopia and Liberia. European rule had significant impacts on Africa's societies, and colonies were maintained for the purpose of economic exploitation and extraction of natural resources. Most present states emerged from a process of decolonisation following World War II, and established the Organisation of African Unity in 1963, the predecessor to the African Union. The nascent countries decided to keep their colonial borders, with traditional power structures used in governance to varying degrees. (Full article...)
Selected article –

Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea, and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area Rio dos Camarões (Shrimp River), which became Cameroon in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate in the north in the 19th century, and various ethnic groups of the west and northwest established powerful chiefdoms and fondoms.
Cameroon became a German colony in 1884 known as Kamerun. After World War I, it was divided between France and the United Kingdom as League of Nations mandates. France took four-fifths and the United Kingdom one-fifth of the territory and both ruled it under mandate until independence in 1960 and 1961 respectively. The Union des Populations du Cameroun (UPC) political party advocated independence but was outlawed by France in the 1950s, leading to the national liberation insurgency fought between French and UPC militant forces until early 1971. In 1960, the French-administered part of Cameroon became independent, as the Republic of Cameroun, under President Ahmadou Ahidjo. The southern part of British Cameroons federated with it in 1961 to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. The federation was abandoned in 1972. The country was renamed the United Republic of Cameroon in 1972 and back to the Republic of Cameroon in 1984 by a presidential decree by President Paul Biya. Biya, the incumbent president, has led the country since 1982 following Ahidjo's resignation; he previously held office as prime minister from 1975 onward. Cameroon is governed as a unitary presidential republic. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that Malabo Mosque cost about two billion Central African CFA francs to build?
- ... that American Olympic rugby player Sarah Levy is the great-granddaughter of a Springbok?
- ... that during the First World War the East African Mounted Rifles sometimes painted stripes on their horses to camouflage them as zebras?
- ... that Michigan defensive end Eyabi Okie, ranked number 3 in the 2018 college football recruiting class, changed his surname from "Anoma" to recognize his mother who lives in Africa?
- ... that South African president Jacob Zuma requested a tour of a Sainsbury's supermarket during his state visit to the United Kingdom in 2010?
- ... that the book Love Falls On Us, about the LGBTQ movement in Africa, was praised by author Uzodinma Iweala for "elevating the extraordinary ordinariness of L.G.B.T.Q. Africans"?
Categories
Selected biography –
William Henry Sheppard (March 8, 1865 – November 25, 1927) was one of the earliest African Americans to become a missionary for the Presbyterian Church. He spent 20 years in Africa, primarily in and around the Congo Free State, and is best known for his efforts to publicize the atrocities committed against the Kuba and other Congolese peoples by King Leopold II's Force Publique.
Sheppard's efforts contributed to the contemporary debate on European colonialism and imperialism in the region, particularly among those of the African-American community. However, it has been noted that he traditionally received little attention in literature on the subject. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
|
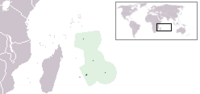
| ||
Mauritius (French: Maurice /mɔʁis/; Mauritian Creole: Moris), officially the Republic of Mauritius (French: République de Maurice), is an island nation off the coast of the African continent in the southwest Indian Ocean, about 900 kilometers (560 mi) east of Madagascar. In addition to the island of Mauritius, the republic includes the islands of St. Brandon, Rodrigues and the Agalega Islands. Mauritius is part of the Mascarene Islands.
Mauritius attained independence in 1968 and became a republic in the Commonwealth of Nations in 1992. It is a parliamentary democracy, with the government headed by the prime minister and a council of ministers. The head of state is the President of Mauritius, who is elected for a five-year term by the National Assembly, the unicameral Mauritian parliament. The National Assembly consists of 62 members elected directly by popular vote, with between four and eight further members appointed from "best losers" election candidates to represent ethnic minorities, if underrepresented after the elections. (Read more...)
Selected city –
Monrovia (/mənˈroʊviə/ ⓘ) is the administrative capital and largest city of Liberia. Founded in 1822, it is located on Cape Mesurado on the Atlantic coast and as of the 2022 census had 1,761,032 residents, home to 33.5% of Liberia’s total population. Its largely urbanized metro area, including Montserrado and Margibi counties, was home to 2,225,911 inhabitants as of the 2022 census.
As the nation's primary city, Monrovia is the country's economic, financial and cultural center; its economy is primarily centered on its harbor and its role as the seat of Liberian government. The city's economy is largely based on its position as chief Atlantic port of Liberia, with the Freeport of Monrovia based in the city being the largest and main port in the country. (Full article...)
In the news
- 10 April 2025 – Land reform in Zimbabwe
- Zimbabwe begins issuing the first financial compensation payments to White Zimbabwean farmers whose farms were seized by Robert Mugabe's government between 2000 and 2002. A total of 740 farmers will be compensated as per the 2020 agreement with the Commercial Farmers' Union. (BBC News)
- 8 April 2025 –
- The death toll from the heavy flooding in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, caused by overflow of the Ndjili River increases to 33 deaths. Hundreds of buildings are completely submerged and thousands of people are trapped in their homes. (NPR) (DW)
- About 50 hippos are killed by anthrax poisoning at Virunga National Park in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. (CTV News)
- 8 April 2025 – 2024 Democratic Republic of the Congo coup attempt, Democratic Republic of the Congo–United States relations
- Three U.S. citizens have their sentences for attempting a coup against the Congolese President Félix Tshisekedi in 2024 commuted and are extradited back to the United States. They were previously sentenced to death along with 34 others for the failed attempt that killed six people, including the coup's leader Christian Malanga. (NPR)
- 7 April 2025 – Herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria
- The National Emergency Management Agency reports that at least 52 people have been killed and over 2,000 others have been displaced from their homes in recent days in tit for tat attacks by rival herders over control of arable land in Plateau State, Nigeria. (Reuters)
- 7 April 2025 – Algeria–Mali relations
- Algeria bans flights to and from Mali in response to "recurrent violations" of Algerian airspace by Malian military drones. (Reuters)
Updated: 11:05, 11 April 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –
- ... that Liberia College in the country of Liberia was authorized by the legislature in 1851, but did not start classes until 1863?
- ... that the forced removal of 700,000 people from slums in Zimbabwe in 2005 was called "a crime against humanity" by the UN?
- ... that the supreme god of the southern African Bushmen is Cagn, a trickster who shapeshifts into a praying mantis?
- ... that Bahá'í Faith in Niger began during a period of wide scale growth in the religion across Sub-Saharan Africa near the end of its colonial period?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























































































